S e c t i o n I I I . G E N E R A L M A I N T E N A N C E I N S T R U C T I O N S
S C O P E
This section contains safety warnings, guidelines and general maintenance instructions. They should be
followed when doing maintenance procedures.
PREPARATION FOR MAINTENANCE
a. PERSONNEL SAFETY. Practice all shop safety procedures and read all warnings in this manual.
b. PROPER EQUIPMENT.Get equipment before starting a maintenance task. See page 2-1, the
RPSTL, TM 9-2350-261-24P, and the maintenance tasks for tools, equipment, parts, and materials.
c. WHAT To DISCARD. Parts to discard, such as lock washers, locknuts, and gaskets are listed in the
maintenance task. If the step does not say to discard a part, the part should be saved. It may be used later
or be repaired.
d. HANDLING TECHNIQUES.
(1) Avoid damage to parts during disassembly, cleaning, inspection, repair, and reassembly procedures.
Nick, scratches, and dents caused by carelees handling could result in equipment failure.
(2) Dirt can damage parts and cause malfunctions. Make sure all air and fluid openings, lines, and hoses
are capped or plugged during maintenance procedures.
e. IDENTIFICATION.
(1) During disassembly, tag parts to ensure proper assembly.
(2) During disassembly, tag leads on electrical parts to ensure proper assembly. Tag each lead, as it is
removed, with numbers from wiring diagrams and terminals.
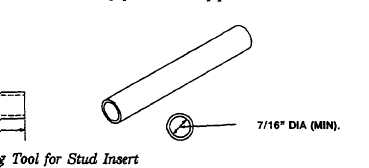
f. FABRICATED TOOLS. These steps enable direct support. and general support personnel to fabricate the
tools locally. Accompanying illustrations below show materials required for fabrication of the tools.
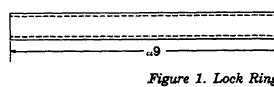
(1) Lock Ring Tool for Stud Insert
Make from round steel stock (1020 or 1040) or locally procure steel pipe.
Remove all burrs.
Do not break sharp edges.
All dimensions are in inches.
2-4/(2-5 and 2-6 deleted)
Change 4